lv apical thrombus treatment|left ventricular mural thrombus : 2024-10-22 ¢= @bp ‹ d©Y©_!@»ƒ¬ø˜lêf¶×Gb3æ unyKÒÙr® ƒ ¾îãI¾˜^ . I came across this post while looking for the layaway plan cuz EDC still hasn’t cancelled my camping or GA ticket despite nonpayment since December. I’ve received several emails but so far no action. I think the current economy changed a lot of people’s plans and EDC is hesitant to cancel.
0 · mural thrombus of cardiac apex
1 · lv thrombus treatment guidelines nhs
2 · lv thrombus anticoagulation
3 · left ventricular thrombus symptoms
4 · left ventricular thrombus management
5 · left ventricular mural thrombus
6 · chest guidelines lv thrombus
7 · aha guidelines lv thrombus
These are, the stages of EDC LV 2014. kineticFIELD. The largest stage of any Insomniac production, ever. Nicknamed by Headliners as “the temple of happiness” and “The Cathedral of EDM,” at 440 feet wide, 80 feet tall, with 1,000 lighting fixtures, 30 lasers, and requiring 2.5 million watts of power, this is kineticFIELD.
lv apical thrombus treatment*******The 2019 AHA/ASA guideline for the early management of patients with acute ischemic stroke states that in patients with major ischemic stroke likely to produce severe disability and known LV thrombus, treatment with IV alteplase may be .left ventricular mural thrombus¢= @bp ‹ d©Y©_!@»ƒ¬ø˜lêf¶×Gb3æ unyKÒÙr® ƒ ¾îãI¾˜^ .
We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us.¢= @bp ‹ d©Y©_!@»ƒ¬ø˜lêf¶×Gb3æ unyKÒÙr® ƒ ¾îãI¾˜^ .Left ventricular (LV) thrombus formation is a well‐known complication in the course of .

eLetters should relate to an article recently published in the journal and are not a .We sought to determine whether an association existed between the .
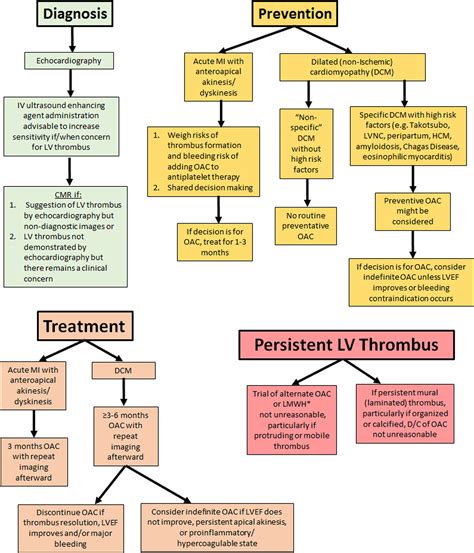
Left ventricular (LV) thrombus may develop after acute myocardial infarction (MI) and occurs most often with a large, anterior ST-elevation MI (STEMI). However, the .
A small prospective study (n=26) showed that enoxaparin 100 IU/kg twice a day, followed by fluindione treatment decreased thrombus size and resulted in . On the basis of limited data, patients with nonischemic cardiomyopathy with LV thrombus should be treated with OAC for at least 3–6 months, with discontinuation if .
Etiology and Treatment of LV Thrombus. Cumulative etiologies (A) and long-term anticoagulants (B) selected for treatment of left ventricular .The 2013 American College of Cardiology Foundation/AHA STEMI guidelines recommend as reasonable (Class 2a, Level of Evidence: C) 3 months of VKA therapy for patients with STEMI and asymptomatic LV .
Standard transthoracic echocardiography (TTE) is typically the screening modality of choice for LV thrombus detection and should be performed within 24 hours of .
Therapies to prevent and treat LV thrombus following AMI also target Virchow’s triad. Guideline-directed medical therapy addresses issues of blood stasis, .
The 2019 AHA/ASA guideline for the early management of patients with acute ischemic stroke states that in patients with major ischemic stroke likely to produce severe disability and known LV thrombus, treatment with IV alteplase may be reasonable (Class of Recommendation IIb; Level of Evidence C-LD). 110 On the basis of consensus . Left ventricular (LV) thrombus may develop after acute myocardial infarction (MI) and occurs most often with a large, anterior ST-elevation MI (STEMI). However, the use of reperfusion therapies, including percutaneous coronary intervention and fibrinolysis, has significantly reduced the risk.
A small prospective study (n=26) showed that enoxaparin 100 IU/kg twice a day, followed by fluindione treatment decreased thrombus size and resulted in resolution of thrombi in 73% of the patients, suggesting that this therapy may be as effective as unfractionated heparin at 3 weeks.
On the basis of limited data, patients with nonischemic cardiomyopathy with LV thrombus should be treated with OAC for at least 3–6 months, with discontinuation if LV ejection fraction improves to >35% (assuming resolution of the LV thrombus) or if major bleeding occurs.lv apical thrombus treatmentEtiology and Treatment of LV Thrombus. Cumulative etiologies (A) and long-term anticoagulants (B) selected for treatment of left ventricular (LV) thrombus. In-hospital mortality was 7.8%. An additional 7.8% were not initiated on long-term anticoagulation due to medical contraindications.The 2013 American College of Cardiology Foundation/AHA STEMI guidelines recommend as reasonable (Class 2a, Level of Evidence: C) 3 months of VKA therapy for patients with STEMI and asymptomatic LV mural thrombus with a target INR of 2.0-2.5 when combining OAC with DAPT. 5 The 2014 AHA/American Stroke Association stroke guidelines .
Standard transthoracic echocardiography (TTE) is typically the screening modality of choice for LV thrombus detection and should be performed within 24 hours of admission in those at high risk for apical LV thrombus (e.g., those with large or anterior MI or those receiving delayed reperfusion). Therapies to prevent and treat LV thrombus following AMI also target Virchow’s triad. Guideline-directed medical therapy addresses issues of blood stasis, while anticoagulation addresses hypercoagulability and reperfusion therapy ± anti-inflammatory therapy addresses tissue injury.With randomized clinical trials investigating the optimal antithrombotic regimen in patients with MI who require concomitant chronic anticoagulation and with the emergence of the direct-acting oral anticoagulants, treatment options for post-MI LV thrombus have become more complicated. INTRODUCTION. Left ventricular (LV) thrombus may develop after acute myocardial infarction (MI) and occurs most often with a large, anterior ST-elevation MI (STEMI). However, the use of reperfusion therapies, including percutaneous coronary intervention and fibrinolysis, has significantly reduced the risk. The 2019 AHA/ASA guideline for the early management of patients with acute ischemic stroke states that in patients with major ischemic stroke likely to produce severe disability and known LV thrombus, treatment with IV alteplase may be reasonable (Class of Recommendation IIb; Level of Evidence C-LD). 110 On the basis of consensus .
Left ventricular (LV) thrombus may develop after acute myocardial infarction (MI) and occurs most often with a large, anterior ST-elevation MI (STEMI). However, the use of reperfusion therapies, including percutaneous coronary intervention and fibrinolysis, has significantly reduced the risk.
A small prospective study (n=26) showed that enoxaparin 100 IU/kg twice a day, followed by fluindione treatment decreased thrombus size and resulted in resolution of thrombi in 73% of the patients, suggesting that this therapy may be as effective as unfractionated heparin at 3 weeks.
On the basis of limited data, patients with nonischemic cardiomyopathy with LV thrombus should be treated with OAC for at least 3–6 months, with discontinuation if LV ejection fraction improves to >35% (assuming resolution of the LV thrombus) or if major bleeding occurs.lv apical thrombus treatment left ventricular mural thrombusEtiology and Treatment of LV Thrombus. Cumulative etiologies (A) and long-term anticoagulants (B) selected for treatment of left ventricular (LV) thrombus. In-hospital mortality was 7.8%. An additional 7.8% were not initiated on long-term anticoagulation due to medical contraindications.
The 2013 American College of Cardiology Foundation/AHA STEMI guidelines recommend as reasonable (Class 2a, Level of Evidence: C) 3 months of VKA therapy for patients with STEMI and asymptomatic LV mural thrombus with a target INR of 2.0-2.5 when combining OAC with DAPT. 5 The 2014 AHA/American Stroke Association stroke guidelines .
Standard transthoracic echocardiography (TTE) is typically the screening modality of choice for LV thrombus detection and should be performed within 24 hours of admission in those at high risk for apical LV thrombus (e.g., those with large or anterior MI or those receiving delayed reperfusion). Therapies to prevent and treat LV thrombus following AMI also target Virchow’s triad. Guideline-directed medical therapy addresses issues of blood stasis, while anticoagulation addresses hypercoagulability and reperfusion therapy ± anti-inflammatory therapy addresses tissue injury.
EDC Las Vegas 2024 is streaming online for free all weekend via the Insomniac YouTube page and the Insomniac website . Starting at 6:30 p.m. PT Friday, four separate livestreams will be available .
lv apical thrombus treatment|left ventricular mural thrombus